German Invasion Of Luxembourg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The German invasion of Luxembourg was part of
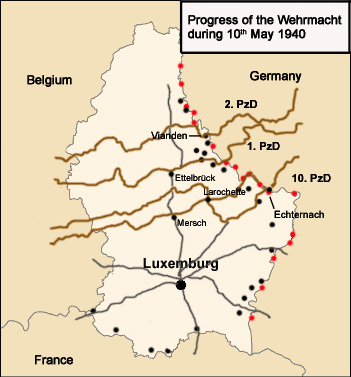 The German invasion began at 04:35 when the 1st, 2nd, and 10th Panzer Divisions crossed the border at
The German invasion began at 04:35 when the 1st, 2nd, and 10th Panzer Divisions crossed the border at  Following consultation with her ministers, Grand Duchess Charlotte decided to abandon the palace. Accompanied by her husband, Prince Felix, her mother, Dowager Grand Duchess Marie Anne, and members of the Grand-Ducal suite, she departed for the border village of
Following consultation with her ministers, Grand Duchess Charlotte decided to abandon the palace. Accompanied by her husband, Prince Felix, her mother, Dowager Grand Duchess Marie Anne, and members of the Grand-Ducal suite, she departed for the border village of
Case Yellow
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
(german: Fall Gelb), the German invasion of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
—Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
—and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The battle began on 10 May 1940 and lasted just one day. Facing only light resistance, German troops quickly occupied Luxembourg. The Luxembourgish government, and Grand Duchess Charlotte
Charlotte (Charlotte Adelgonde Elisabeth Marie Wilhelmine; 23 January 1896 – 9 July 1985) reigned as Grand Duchess of Luxembourg from 14 January 1919 until her abdication on 12 November 1964.
She acceded to the throne on 14 January 1919 foll ...
, managed to escape the country and a government-in-exile was created in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
.
Background
On 1 September 1939Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
invaded Poland, initiating World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. This put Luxembourg's Grand Ducal government in a delicate situation. On the one hand, the population's sympathies laid with the UK and France; on the other hand, due to the country's policy of neutrality since the Treaty of London in 1867, the government adopted a careful non-belligerent
A non-belligerent is a person, a state, or other organization that does not fight in a given conflict. The term is often used to describe a country that does not take part militarily in a war.
A non-belligerent state differs from a neutral one i ...
stance towards its neighbours. In accordance with the treaty's restrictions, the only military force Luxembourg maintained was its small Volunteer Corps under Captain Aloyse Jacoby
Aloys(e) Jacoby (1895, Echternach - 1965) was a Luxembourgish Colonel who served during World War Two.
Early life and pre-Second World War
Aloyse Jacoby's parents are unknown, he was born sometime in 1895, according to his records from Dachau, a ...
, reinforced by the Grand Ducal Gendarmerie The Grand Ducal Gendarmerie (french: Gendarmerie Grand-Ducale; Luxembourgish: ''Groussherzoglech Gendarmerie'') was the national Gendarmerie force of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, carrying both civil and military duties. It merged on January 1st, 2 ...
under Captain Maurice Stein. Together they formed the '' Corps des Gendarmes et Volontaires'' under Major-Commandant Émile Speller
Émile Speller (7 October 1875 – 17 January 1952) was a Luxembourgish military officer and the commander of the country's Gendarmes and Volunteers Corps (''Corps des Gendarmes et Volontaires'') during the German invasion of Luxembourg in World ...
.
At noon on 1 September Radio Luxembourg
Radio Luxembourg was a multilingual commercial broadcaster in Luxembourg. It is known in most non-English languages as RTL (for Radio Television Luxembourg).
The English-language service of Radio Luxembourg began in 1933 as one of the earlies ...
announced that in order for the country to remain unambiguously neutral it would cease broadcasting. Exceptions were a daily 20 minute-long message at midday and in the evening reserved for government announcements. For the rest of the month, the government supplied full transcripts of its broadcasts to the foreign legations in the country. Later that day several German stations posed as Radio Luxembourg by broadcasting in the Luxembourgian wavelength, making, in the opinion of United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
Chargé d'Affaires
A ''chargé d'affaires'' (), plural ''chargés d'affaires'', often shortened to ''chargé'' (French) and sometimes in colloquial English to ''charge-D'', is a diplomat who serves as an embassy's chief of mission in the absence of the ambassador ...
George Platt Waller
George Platt Waller Jr. (September 7, 1889 – February 26, 1962) was an American diplomat and the United States chargé d'affaires in Luxembourg during World War II.
Biography Early life
George Platt Waller Jr. was born to George Platt and S ...
, "grossly unneutral announcements". On the evening of 21 September, the Grand Ducal government suspended all broadcasts pending the resolution of the war.
On 14 September the volunteer corps was bolstered by the addition of a 125-strong auxiliary unit. German military manoeuvres and river traffic made the population increasingly nervous, so in the spring of 1940 fortifications were erected along the borders with Germany and France. The so-called Schuster Line
The Schuster Line ( lb, Schuster-Linn) was a line of barriers and barricades erected by the Luxembourg government along its borders with Germany and France shortly before World War II. The line was named after Joseph Schuster, Luxembourg's chief en ...
, named after its chief constructor, consisted of 41 sets of concrete blocks and iron gates; 18 bridgeblocks on the German border, 18 roadblocks on the German border, and five roadblocks on the French border. Since the ''Corps des Gendarmes et Volontaires'' had no pioneer
Pioneer commonly refers to a settler who migrates to previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited land.
In the United States pioneer commonly refers to an American pioneer, a person in American history who migrated west to join in settling and de ...
unit, construction fell to the responsibility of civilian engineers, while technical advice was sought from the French, who took great interest in the line's establishment. A series of nine radio outposts were established along the German border, each manned by gendarmes, with a central radio receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. Th ...
in Captain Stein's official office near the volunteers' Saint-Esprit Barracks in the capital. On 4 January 1940, the Cabinet convened under Grand Duchess Charlotte
Charlotte (Charlotte Adelgonde Elisabeth Marie Wilhelmine; 23 January 1896 – 9 July 1985) reigned as Grand Duchess of Luxembourg from 14 January 1919 until her abdication on 12 November 1964.
She acceded to the throne on 14 January 1919 foll ...
and outlined steps to be taken in the event of a German invasion. Charlotte decided that if possible she and the government would flee abroad in the event of an attack to advocate for the country's sovereignty. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, her elder sister and then-Grand Duchess Marie-Adélaïde had elected to stay during Germany's occupation of the country, bringing the monarchy into disrepute; Charlotte wanted to avoid such problems. The government moved some of the country's gold reserves to Belgium, and began stockpiling funds in its Brussels and Paris legations in the event it was forced to flee due to German attack. The Paris legation was also given a sealed envelope detailing a formal request of military assistance from the French government in case communications were cut-off in an invasion.
After several false alarms in the spring of 1940, the probability of a military conflict between Germany and France grew. Germany stopped the export of coke for the Luxembourgish steel industry
In the industrial sector, the Luxembourg steel industry continues to occupy the first place in the country, even after the industrial reforms which have taken place since the 1960s.
History Early development
Iron was already worked and processed ...
. Abwehr agents under Oskar Reile infiltrated the country, posing as tourists.Horne, Alistair
Sir Alistair Allan Horne (9 November 1925 – 25 May 2017) was a British journalist, biographer and historian of Europe, especially of 19th- and 20th-century France. He wrote more than 20 books on travel, history, and biography.
Early life, ...
, ''To Lose a Battle'', p.258-264 This was observed by Captain Fernand Archen, an undercover senior French intelligence officer in Luxembourg City
Luxembourg ( lb, Lëtzebuerg; french: Luxembourg; german: Luxemburg), also known as Luxembourg City ( lb, Stad Lëtzebuerg, link=no or ; french: Ville de Luxembourg, link=no; german: Stadt Luxemburg, link=no or ), is the capital city of the Lu ...
, posing as a wine merchant. He reported his findings to his superiors at Longwy
Longwy (; older german: Langich, ; lb, label= Luxemburgish, Lonkech) is a commune in the French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle, Lorraine, administrative region of Grand Est, northeastern France.
The inhabitants are known as ''Longoviciens'' ...
on 7 May, understanding that the agents were to be used to seize key bridges over the Sauer
The Sauer (German and Luxembourgish, , ) or Sûre ( French, ) is a river in Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany. A left tributary of the Moselle, its total length is .
Rising near Vaux-sur-Sûre in the Ardennes in southeastern Belgium, the Sauer ...
, Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; german: Mosel ; lb, Musel ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it jo ...
and Our
Our or OUR may refer to:
* The possessive form of " we"
* Our (river), in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany
* Our, Belgium, a village in Belgium
* Our, Jura, a commune in France
* Office of Utilities Regulation (OUR), a government utility regulato ...
rivers. Luxembourg authorities also took notice, and Captain Stein worked to stop the Germans' activities. On 3 March, the French Third Army The Third Army (french: IIIe Armée) was a Field army of the French Army, which fought during World War I and World War II.
Commanders World War I
*General Ruffey (Mobilization – 30 August 1914)
*General Sarrail (30 August 1914 – 22 July 1915 ...
was ordered to occupy Luxembourg in the event of a German attack.
Prelude
On the evening of 8 May, the Grand Ducal Government ordered for the first time that all doors of the Schuster Line be closed at 11:00 and remain so regardless of circumstance until 06:00 the following morning. Throughout the day Luxembourgian authorities witnessed much less activity on the far side of the border and made no reports of tank or machine gun movements. On the afternoon of 9 May, a French intelligence officer stationed inClervaux
Clervaux (; lb, Clierf or (locally) ; german: Clerf) is a commune and town in northern Luxembourg, administrative capital of the canton of Clervaux.
The town's arms, granted in 1896, show three blackbirds on a gold ground in the chief of a red ...
witnessed German troops preparing pontoon bridges in the Sauer. He attempted in vain to contact Captain Archen, and resorted to making a direct phone call to his superiors at Longwy. Also that day a German national working in Luxembourg as a gardener and a member of the German fifth column
A fifth column is any group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. According to Harris Mylonas and Scott Radnitz, "fifth columns" are “domestic actors who work to un ...
warned his Luxembourgish employer, Carlo Tuck, that an invasion was impending. Tuck passed the warning on to government officials. Late that evening, the Grand Ducal government came into possession of a document from a German divisional command. Dated 23 April 1940, it detailed the division's chief of staff's orders to various units to occupy strategic points within the country. The Grand Ducal government put all border posts and Grand Ducal Gendarmerie stations on full alert. In Luxembourg City, gendarmes mobilised to defend public buildings and dispatched vehicle patrols to arrest fifth columnists. The economic councillor and the chancellor of the German legation were detained for questioning regarding allegations that they had used legation cars to organise subversive activities within the country. Since an invasion had not yet occurred they still enjoyed diplomatic privilege and the police were forced to release them. One group of fifth columnists was arrested while attempting to reach the legation. Meanwhile, Captain Archen had received his subordinate's report, but by that point, he had been told by informants in the Gendarmerie that shots had been exchanged with German operatives at a remote farm near the Moselle. At 11:45 on 9 May he radioed Longwy: "Reports of important German troop movements on the German-Luxembourg frontier." Throughout the night his messages became more and more frantic. Two Luxembourgish customs officials at Wormeldange
Wormeldange ( lb, Wuermer or (locally) ; german: Wormeldingen) is a commune and small town in eastern Luxembourg. It is part of the canton of Grevenmacher.
, the town of Wormeldange, which lies in the south of the commune, has a population of 7 ...
heard horses and soldiers across the Moselle, but were unable to make out the Germans' activities due to heavy fog.
At around midnight, Captain Stein, Minister of Justice Victor Bodson
Victor Nicolas Bodson (24 March 1902 – 29 June 1984) was a Luxembourgish politician and lawyer who held a number of political posts during his career. He is recognised as Righteous Among the Nations awarded by Yad Vashem for his actions during ...
, and Police Commissioner Joseph Michel Weis held an emergency meeting. Bodson requested that the capital be reinforced by gendarmes from the south, and told Weis to forward this information to the capital's district commissioner to give the necessary orders. Weis later tried to contact the district commissioner by phone, but failed to reach him; reinforcements never came. A short time later the gendarmes at Diekirch were ordered to patrol the local railway bridge and be wary of unfamiliar persons. Luxembourgian authorities received the first reports of exchanged fire at around 02:00 on 10 May when two gendarmes were ambushed near the German border by plainclothes agents. The Germans retreated to the Fels mill near Grevenmacher
Grevenmacher (; ) is a commune with town status in eastern Luxembourg, near the border with Germany. It gives its name to and is the capital of the canton of Grevenmacher, and, until its abolition in 2015, the district of Grevenmacher. The town ...
and around 20 soldiers who volunteered were dispatched to arrest them. The government then ordered all steel doors along the border locked. At 02:15 soldiers stationed in Bous were attacked by Germans in civilian clothes. One soldier was badly injured, as was one German who was detained. Shortly thereafter a gendarmerie lieutenant and his chauffeur were ambushed and exchanged fire with German-speaking cyclists; no one was hurt. Fifth columnists successfully severed the telephone wires between the capital and the border posts, forcing the gendarmes to communicate via shortwave radio. German agents gradually seized the radio stations; the last post to fall, in Wasserbillig, transmitted until the Germans breached the operating room.
The steel doors of the Schuster Line were ordered closed on 10 May 1940 at 03:15, following reports of movement of German troops on the east side of the border rivers Our, Sauer, and Moselle. At 03:30 Luxembourgian authorities released interned French pilots and German deserters. The Royal Family was evacuated from its residence in Colmar-Berg
Colmar-Berg ( lb, Colmer-Bierg, german: Colmar-Berg) is a commune and town in central Luxembourg, in the canton of Mersch. It is situated at the confluence of the rivers Attert and Alzette.
Colmar-Berg is the site of the Grand Duke of Luxembourg ...
to the Grand Ducal palace
The Grand Ducal Palace ( lb, Groussherzogleche Palais, french: Palais grand-ducal, german: Großherzogliches Palais) is a palace in Luxembourg City, in southern Luxembourg. It is the official residence of the grand duke of Luxembourg, and wher ...
in Luxembourg City. Around 30 minutes later, at dawn, German planes were spotted flying over Luxembourg City towards Belgium.
Invasion
 The German invasion began at 04:35 when the 1st, 2nd, and 10th Panzer Divisions crossed the border at
The German invasion began at 04:35 when the 1st, 2nd, and 10th Panzer Divisions crossed the border at Wallendorf-Pont
Wallendorf-Pont (, ) is a village in the commune of Reisdorf, in eastern Luxembourg. , the town has a population of 83.
It is located on the Sauer river, on the border with Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germa ...
, Vianden
Vianden ( lb, Veianen or (locally) ) is a commune with town status in the Oesling, north-eastern Luxembourg, with over 1,800 inhabitants. It is the capital of the canton of Vianden, which is part of the district of Diekirch. Vianden lies on t ...
, and Echternach
Echternach ( lb, Iechternach or (locally) ) is a commune with town status in the canton of Echternach, which is part of the district of Grevenmacher, in eastern Luxembourg. Echternach lies near the border with Germany, and is the oldest town in L ...
respectively. Wooden ramps were used to cross over the Schuster Line's tank traps. Fire was exchanged, but the Germans did not encounter any significant resistance except for some bridges destroyed and some land mines since the majority of the Luxembourgish Volunteer Corps stayed in their barracks. The border was defended only by soldiers who had volunteered for guard duty and gendarme
Wrong info! -->
A gendarmerie () is a military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to "Man-at-arms, men-at-arms" ...
s. A handful of Germans secured the bridge at Wormeldange and captured the two customs officers there, who had demanded that they halt but refrained from opening fire. The partly demolished bridge over the Sauer at Echternach was quickly repaired by engineers of the Großdeutschland regiment, allowing the passage of the 10th Panzer Division. Planes flew overhead, heading for Belgium and France, though some stopped and landed troops within the country.
Captain Archen repeatedly alerted his superiors at Longwy of the invasion, but his reports never reached the 3rd Army at Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand E ...
. General Charles Condé, the army's commander, was unclear about the situation and at 05:30 dispatched aerial reconnaissance units to investigate. At 06:00 the French 3rd Light Cavalry Division was ordered to intervene.
Telephone and radio messages from the border posts to the Gendarmerie and Volunteer Corps headquarters informed the Luxembourgish government and Grand Ducal court of the invasion. Foreign Minister Joseph Bech
Joseph Bech (17 February 1887 – 8 March 1975)Thewes, Guy"Les gouvernements du Grand-Duché depuis 1848." Service information et presse. Luxembourg: Imprimerie Centrale, 2011. was a Luxembourgish politician and lawyer. He was the 15th Prime Mi ...
, in the presence of Prime Minister Pierre Dupong
Pierre Dupong (1 November 1885 – 23 December 1953)Thewes, Guy"Les gouvernements du Grand-Duché depuis 1848." Service information et presse. Luxembourg: Imprimerie Centrale, 2011. was a Luxembourgish politician and statesman. He was the 16th ...
, attempted to contact the German ambassador at the legation and at his private residence, but they were informed that he was present at neither. At 06:30 the majority of the government, including Dupong and Bech, evacuated the capital by motorcade to the border town of Esch. Bodson stayed behind at the Saint-Esprit Barracks to monitor the situation. In Esch a group of 125 German special operations troops had landed by Fieseler Storch
The Fieseler Fi 156 ''Storch'' (, "stork") was a German liaison aircraft built by Fieseler before and during World War II. Production continued in other countries into the 1950s for the private market. It was notable for its excellent short fie ...
, with orders to hold the area until the main invasion force arrived. A gendarme confronted the soldiers and asked that they leave, but he was taken prisoner. The government motorcade encountered a roadblock at a crossroads manned by German units, and was forced to detour through the countryside to avoid capture. French Ambassador Jean Tripier followed the government party but was stopped by the Germans and forced to return to the capital. Belgian Ambassador Kervyn de Meerendré was also stopped by German soldiers at the border and ordered to turn back, as was the Luxembourgish Minister of Education, Nicolas Margue, who had attempted to escape by taxi. Bodson later fled the capital and, having learned many of the secondary roads by memory, was able to avoid German roadblocks and navigate his way to France.
 Following consultation with her ministers, Grand Duchess Charlotte decided to abandon the palace. Accompanied by her husband, Prince Felix, her mother, Dowager Grand Duchess Marie Anne, and members of the Grand-Ducal suite, she departed for the border village of
Following consultation with her ministers, Grand Duchess Charlotte decided to abandon the palace. Accompanied by her husband, Prince Felix, her mother, Dowager Grand Duchess Marie Anne, and members of the Grand-Ducal suite, she departed for the border village of Redange
Redange or Redange-sur-Attert (; ; ) is a commune and town in northwestern Luxembourg, near the border with Belgium. It is the capital of the canton of Redange. Redange is situated on the river Attert, a tributary of the Alzette.
, the town of ...
. After a brief stop, her party crossed the border at 07:45. Meanwhile, Hereditary Grand Duke Jean and two of his sisters, accompanied by an '' aide-de-camp'', Guillaume Konsbruck Guillaume Konsbruck (3 September 1909 – 3 October 1983) was a Luxembourgish military officer, politician, and manager of the steel company Arbed.
Early life
Guillame Konsbruck was born on 3 September 1909. He studied at the cavalry branch of ...
, were to wait at the border for confirmation of occupation. Around 08:00 the prime minister and his entourage passed over the border before making contact with French troops at Longlaville. Last minute telephone calls with Luxembourg City
Luxembourg ( lb, Lëtzebuerg; french: Luxembourg; german: Luxemburg), also known as Luxembourg City ( lb, Stad Lëtzebuerg, link=no or ; french: Ville de Luxembourg, link=no; german: Stadt Luxemburg, link=no or ), is the capital city of the Lu ...
revealed the capital to be completely surrounded.
Charlotte's party was able to link up with the government motorcade at Longwy. Meanwhile, Jean's party's car was strafed by a German aircraft while stopped at a cafe. Near Esch, the group was delayed by a German roadblock, and they escaped when their chauffeur drove straight through the soldiers. The party ultimately joined Charlotte and the Grand Ducal government at Sainte-Menehould
Sainte-Menehould (; german: Sankt Mathilde) is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France. The 18th-century French playwright Charles-Georges Fenouillot de Falbaire de Quingey (1727–1800) died in Sainte-Ménéhould. It was the ...
.
At 08:00, elements of the French 3rd Light Cavalry Division under General Petiet, supported by the 1st Spahi Brigade under Colonel Jouffault and the 2nd company of the 5th Armoured Battalion, crossed the southern border to conduct a probe of German forces; these units later retreated behind the Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force the ...
. Five Spahi
Spahis () were light-cavalry regiments of the French army recruited primarily from the indigenous populations of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco. The modern French Army retains one regiment of Spahis as an armoured unit, with personnel now ...
s were killed. British Air Marshal Arthur Barratt, impatient with the reluctance of the French Air Force
The French Air and Space Force (AAE) (french: Armée de l'air et de l'espace, ) is the air and space force of the French Armed Forces. It was the first military aviation force in history, formed in 1909 as the , a service arm of the French Army; ...
to conduct air strike
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offic ...
s, ordered a flight of Fairey Battle
The Fairey Battle is a British single-engine light bomber that was designed and manufactured by the Fairey Aviation Company. It was developed during the mid-1930s for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a monoplane successor to the Hawker Hart and Hi ...
bombers from the 226 Squadron to attack German tank columns. They went unescorted and encountered heavy anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
fire. Most were damaged by flak
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
but managed to escape. One received a direct hit and crashed near Bettendorf. German soldiers pulled the three injured crew from the burning wreckage, one of whom later died in a local hospital.
The Grand Ducal Gendarmerie The Grand Ducal Gendarmerie (french: Gendarmerie Grand-Ducale; Luxembourgish: ''Groussherzoglech Gendarmerie'') was the national Gendarmerie force of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, carrying both civil and military duties. It merged on January 1st, 2 ...
resisted the German troops, but to little avail; the capital city was occupied before noon. The Gendarmerie chain of command in the south was thrown into disarray by the influx of refugees and the arrival of German and French troops. Most gendarmes escorted refugees over the border, while some abandoned their posts and fled to France. Total Luxembourgish casualties amounted to six gendarmes and one soldier wounded, while 22 soldiers (six officers and 16 non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s) and 54 gendarmes were captured.
By the evening of 10 May 1940, most of the country, with the exception of the south, was occupied by German forces. More than 90,000 civilians fled from the canton of Esch-sur-Alzette as a consequence of the advance. 47,000 evacuated to France, 45,000 poured into the central and northern part of Luxembourg.
Aftermath
On 11 May the Grand Ducal government reached Paris and installed itself in the Luxembourg legation. Fearing German aerial attack and finding the small facilities unsuitable, the government moved further south, first to Fontainebleau, and thenPoitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomerat ...
. It later moved to Portugal and the United Kingdom, before finally settling in Canada for the duration of the war. In exile, Charlotte became an important symbol of national unity. Her eldest son and heir, Jean
Jean may refer to:
People
* Jean (female given name)
* Jean (male given name)
* Jean (surname)
Fictional characters
* Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character
* Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations
* Jea ...
, volunteered for the British Army in 1942. The only official representative left behind was , head of the Ministry of State Affairs, as well as the 41 deputies.
By the end of May Wehrer and several high ranking functionaries established a provisional "Administrative Commission" to govern Luxembourg in lieu of the Grand Ducal family and the other ministers. Wehrer retained the Ministry of State Affairs and assumed responsibility for Foreign Relations and Justice; Jean Metzdorf held the portfolios for Interior, Transportation, and Public Works; Joseph Carmes managed Finance, Labour, and Public Health; Louis Simmer oversaw Education, and Mathias Pütz directed Agriculture, Viticulture, Commerce, and Industry.
In the days after the invasion Luxembourgian officers walked about the capital freely, though the regular soldiers were mostly confined to their barracks. Colonel Speller was briefly incarcerated by the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one organi ...
, though he was later released under close supervision.
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * {{World War IIinvasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity aggressively enter territory (country subdivision), territory owned by another such entity, gen ...
1940 in Luxembourg
Battles and operations of World War II involving France
Battles and operations of World War II involving Germany
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
Invasions of Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
Germany–Luxembourg military relations
May 1940 events
Battles involving Luxembourg